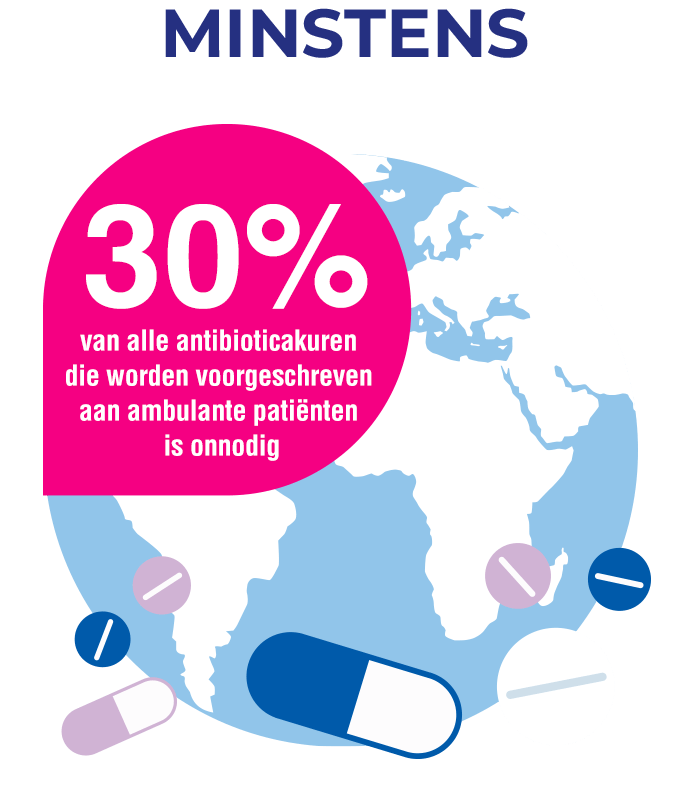
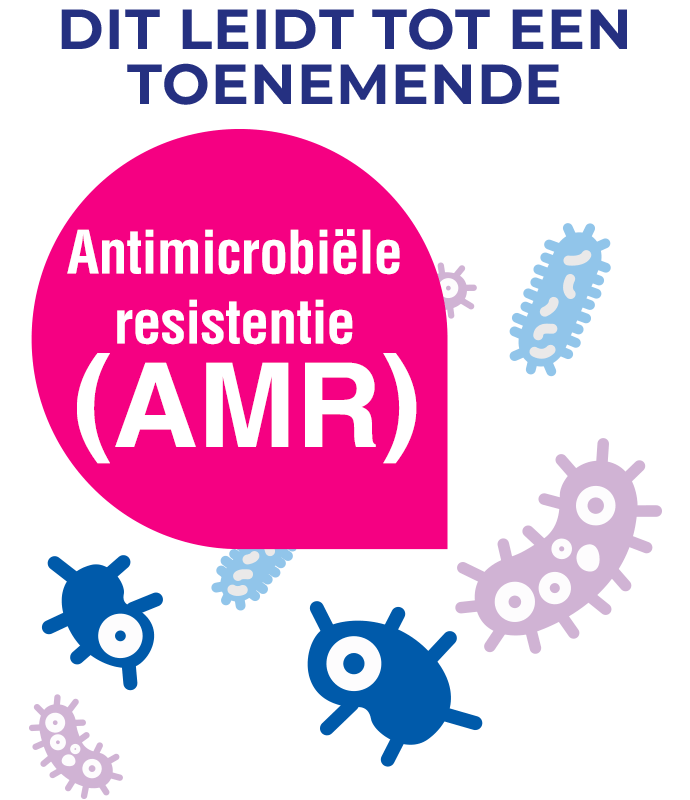


...om de verspreiding van bacteriën met antimicrobiële resistentie te voorkomen, moet het gebruik van antibiotica bij wondzorg aanzienlijk worden verminderd.
Hoewel de Wereldgezondheidsorganisatie AMR aanpakt met een mondiaal actieplan, is er nog veel ruimte om bij te dragen aan de preventie van AMR in de wondzorgsector.1 Om echt doeltreffend op te treden tegen AMR moeten binnen de wondzorg maatregelen worden genomen op elk niveau, van wondspecialisten tot wondverpleegkundigen.
De European Wound Management Association beveelt aan het onnodige gebruik van antibiotica te vermijden a.d.h.v. adequate infectiepreventie en -bestrijding en geschikte hygiëneprotocollen.2
Met de juiste instrumenten voor infectiepreventie en -beheer bij wondzorg kan het onnodige gebruik van antibiotica worden vermeden. Met de merken, Cutimed® en Leukoplast®, heeft Essity een uitgebreid assortiment wondzorgproducten die infectie doeltreffend voorkomen en beheren, zonder bekend risico dat ze verder kunnen bijdragen aan antimicrobiële resistentie.

Cutimed® en Leukoplast® bieden een ruim assortiment werkzame producten voor wondbehandeling en infectiebestrijding die het overmatige gebruik van antibiotica bij wondzorg kunnen helpen vermijden
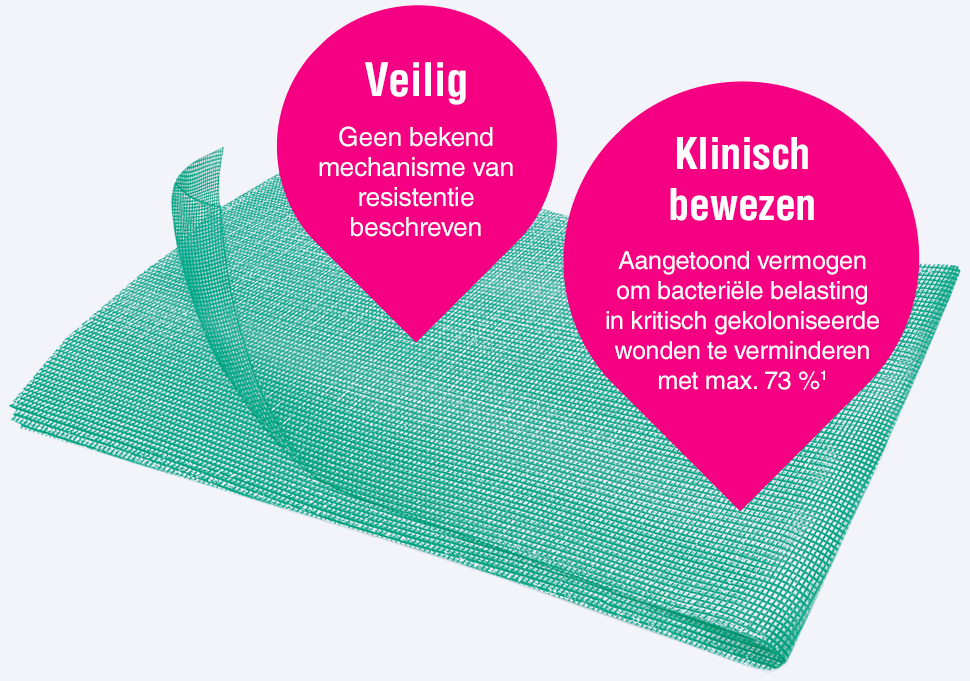
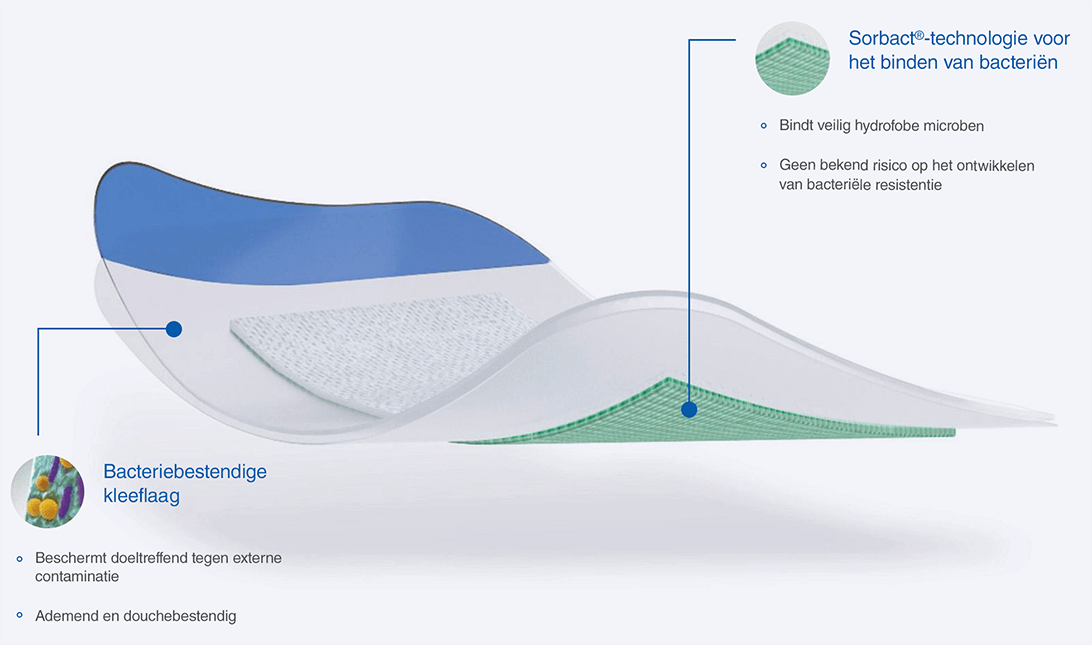
Leukomed® Sorbact® en Cutimed® Sorbact® maken gebruik van de veilige en werkzame Sorbact®-technologie die bacteriën bindt via een puur natuurkundig werkingsmechanisme. Sorbact®-technologie verwijdert bacteriën zonder schadelijke endotoxinen af te geven.3
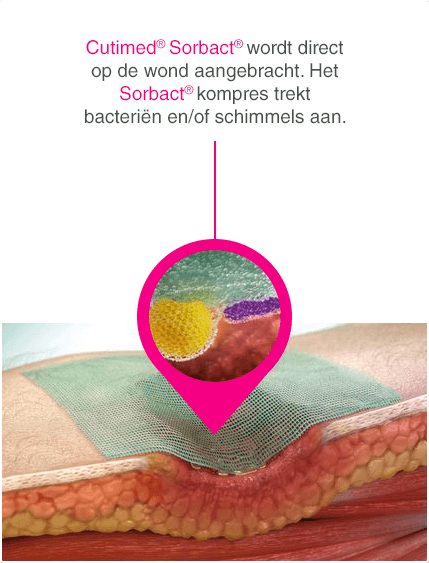
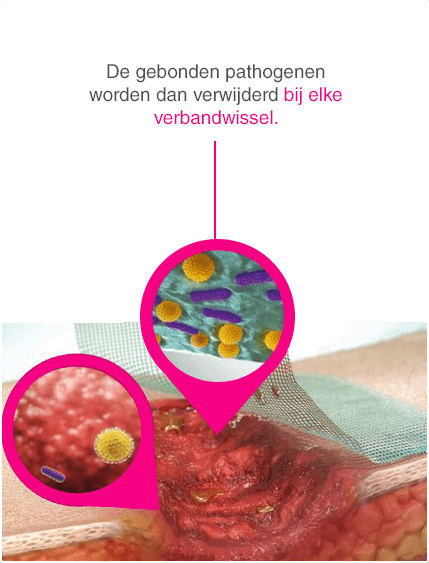
Geavanceerd verband voor chronische wonden om ze effectief te behandelen via een puur natuurkundig werkingsmechanisme.
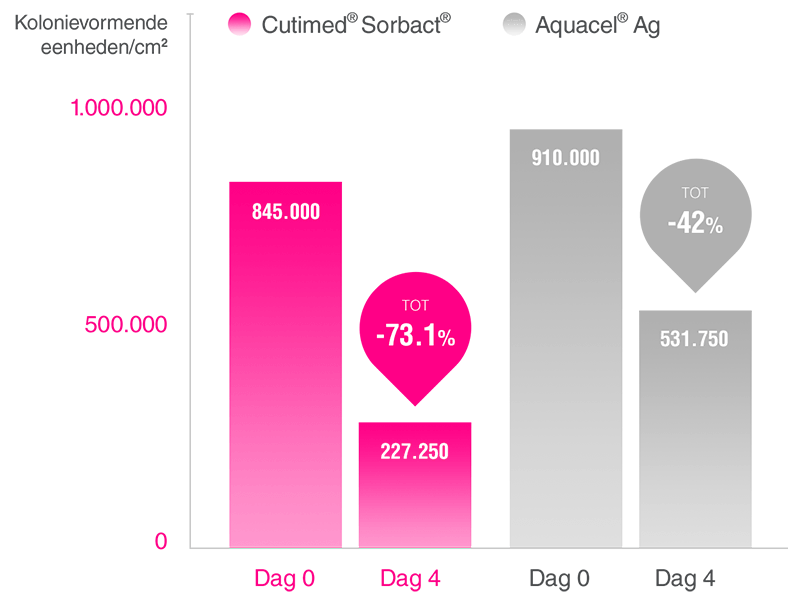
In een gerandomiseerd vergelijkend monocentrisch onderzoek met 40 patiënten met een open been was Cutimed® Sorbact® werkzamer in het verminderen van de kritische kolonisatie dan Aquacel® Ag.8

Innovatief postoperatief verband om bacteriële kolonisatie te verminderen via een puur natuurkundig werkingsmechanisme.
Indicaties
Alle postoperatieve en traumatische wonden met geen tot weinig exsudaat:

Transparant wondverband voor een effectieve beheersing van het infectierisico.

De innovatieve, efficiënte en gebruiksvriendelijke pad voor debridement.

Chirurgisch postoperatief verband om bacteriële kolonisatie te verminderen via een puur natuurkundig werkingsmechanisme.

Eerste spoel- en klemringen ter wereld die actief bacteriën bestrijden.

Infectiemanagement en -beheer voor chronische wonden via een puur natuurkundig werkingsmechanisme.